Online first
Current issue
Archive
Special Issues
About the Journal
Publication Ethics
Anti-Plagiarism system
Instructions for Authors
Instructions for Reviewers
Editorial Board
Editorial Office
Contact
Reviewers
All Reviewers
2024
2023
2022
2021
2020
2019
2018
2017
2016
General Data Protection Regulation (RODO)
RESEARCH PAPER
Perceived life satisfaction of parents raising a child with intellectual disabilities
1
Department of Adapted Physical Activity and Sport, Faculty of Health Sciences, Medical University of Silesia, Katowice,
Poland
2
Department of Medical Anthropology, Faculty of Medical Sciences, Medical University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland
These authors had equal contribution to this work
Corresponding author
Magdalena Maria Gruszczyńska
Department of Medical Anthropology, Faculty of Medical Sciences, Medical University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland
Department of Medical Anthropology, Faculty of Medical Sciences, Medical University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction and objective:
Assessment of life satisfaction is the result of comparing one’s situation with the standards set by oneself. If the comparison result is satisfactory, it results in high satisfaction. Giving birth to a child with an intellectual disability significantly influences parents’ assessment of satisfaction. The aim of the study was to examine the relationship between selected socio-demographic factors and the level of life satisfaction of parents of a child with intellectual disabilities.
Material and methods:
The study included families raising a child with intellectual disabilities. They were parents of students who continued their education in rehabilitation and education centres (OTEW) and special schools. A total of 1,216 parents participated in a paper and electronic survey. The questionnaires included the Satisfaction with Life Scale (SWLS) in Juczynski’s Polish adaptation, and a questionnaire containing questions concerning socio-demographic data.
Results:
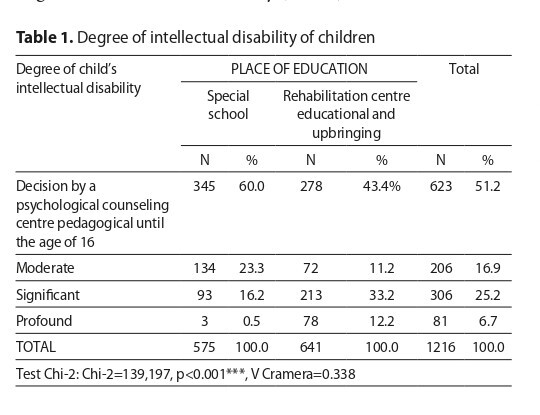
Analysis showed that 58% of parents rated their satisfaction as low. Parents of children from special schools rated satisfaction higher. A higher level of educational correlated positively with life satisfaction. There was no relationship between the age of the child and gender on life satisfaction of the parents.
Conclusions:
Integrated actions should be taken to increase the level of life satisfaction among parents of children with intellectual disabilities. Measures should include psychological support in difficult situations, financial assistance, and employment flexibility (tailored to the parent’s capabilities). An important factor is to promote the acceptance and integration of people with disabilities in society, including in schools, workplaces and local communities, to reduce parents’ feelings of isolation.
Assessment of life satisfaction is the result of comparing one’s situation with the standards set by oneself. If the comparison result is satisfactory, it results in high satisfaction. Giving birth to a child with an intellectual disability significantly influences parents’ assessment of satisfaction. The aim of the study was to examine the relationship between selected socio-demographic factors and the level of life satisfaction of parents of a child with intellectual disabilities.
Material and methods:
The study included families raising a child with intellectual disabilities. They were parents of students who continued their education in rehabilitation and education centres (OTEW) and special schools. A total of 1,216 parents participated in a paper and electronic survey. The questionnaires included the Satisfaction with Life Scale (SWLS) in Juczynski’s Polish adaptation, and a questionnaire containing questions concerning socio-demographic data.
Results:
Analysis showed that 58% of parents rated their satisfaction as low. Parents of children from special schools rated satisfaction higher. A higher level of educational correlated positively with life satisfaction. There was no relationship between the age of the child and gender on life satisfaction of the parents.
Conclusions:
Integrated actions should be taken to increase the level of life satisfaction among parents of children with intellectual disabilities. Measures should include psychological support in difficult situations, financial assistance, and employment flexibility (tailored to the parent’s capabilities). An important factor is to promote the acceptance and integration of people with disabilities in society, including in schools, workplaces and local communities, to reduce parents’ feelings of isolation.
REFERENCES (20)
1.
An HY, Chen W, Wang CW, et al. The Relationships between Physical Activity and Life Satisfaction and Happiness among Young, Middle-Aged, and Older Adults. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(13):4817. doi:10.3390/ijerph17134817.
2.
Vaz CT, de Souza Andrade AC, Proietti FA, et al. A multilevel model of life satisfaction among old people: Individual characteristics and neighborhood physical disorder. BMC Public Health. 2019;19:861. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889....
3.
Parvizi A, Haddadi S, Ghorbani Vajargah P, et al. A systematic review of life satisfaction and related factors among burns patients. Int Wound J. 2023;20(7):2830–2842. doi:10.1111/iwj.14120.
4.
Medvedev ON, Landhuis CE. Exploring constructs of well-being, happiness and quality of life. Peer J. 2018;6(2):2–16.
5.
Mohsen J, Jovanovic V. Similarities and differences in predictors of life satisfaction across age groups: A 150-country study. J Health Psychol. 2021;26(3):401–411. doi:10.1177/1359105318819054.
6.
Juczyński Z. Narzędzia pomiaru w promocji psychologii zdrowia, Warszawa: Pracownia Testów Psychologicznych; 2001.
7.
Emerson SD, Guhn M, Gadermann AM. Measurement invariance of the Satisfaction with Life Scale: reviewing three decades of research. Qual Life Res. 2017;26(9):2251–2264. doi:10.1007/s11136-017-1552-2.
8.
Halstead EJ, Griffith GM, Hastings RP. Social support, coping, and positive perceptions as potential protective factors for the well-being of mothers of children with intellectual and developmental disabilities. Int J Dev Disabil. 2017;26;64(4–5):288–296. https://doi.org/10.1080/204738....
9.
American Psychiatric Association, Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-V), Washington DC, 2023.
10.
International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, ICD-10, WHO 2009.
11.
Scherer N, Verhey I, Kuper H. Depression and anxiety in parents of children with intellectual and developmental disabilities: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2019 Jul 30;14(7):e0219888. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0219888.
12.
Marrus N, Hall L. Intellectual Disability and Language Disorder. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am. 2017;26(3):539–554.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chc.....
13.
Roopani R, Dumka N, Kotwal A. Factors influencing life satisfaction and discrimination among the elderly in India. Indian J Public Health. 2022;66(3):362–366. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijph.i....
14.
Janiszewska M, Barańska A, Jędrych T, et al. The impact of selected factors on acceptance of illness and life satisfaction among female residents of rural areas treated for osteoporosis. Ann Agric Environ Med. 2019;26:592–599. https://doi.org/10.26444/aaem/....
15.
Grzyb B. Uwarunkowania związane z przenoszeniem uczniów niepełnosprawnych ze szkół integracyjnych do specjalnych. Kraków Impuls. 2018:19–39.
16.
Moriwaki M, Yuasa H, Kakehashi M, et al. Impact of social support for mothers as caregivers of cerebral palsy children in Japan. J Pediatr Nurs. 2022;63:e64-e71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pedn....
17.
Sartore GM, Pourliakas A, Lagioia V. Peer support interventions for parents and carers of children with complex needs. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021;12(12):CD010618. https://doi.org/10.1002/146518....
18.
Samadi SA, Abdollahi-Boghrabadi G, McConkey R. Parental Satisfaction with Caregiving for Children with Developmental Disabilities: Development of a New Assessment Tool. Children. 2018;5(12):166. https://doi.org/ 10.3390/children5120166.
19.
Kim HS, Lee CE, Kim KM. Challenges of single parents raising children with intellectual and developmental disabilities. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2023 Jul;36(4):777–786. doi:10.1111/jar.13093.
20.
Staunton E, Kehoe C, Sharkey L. Families under pressure: stress and quality of life in parents of children with an intellectual disability. Ir J Psychol Med. 2023 Jun;40(2):192–199. doi:10.1017/ipm.2020.4.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.