Online first
Current issue
Archive
Special Issues
About the Journal
Publication Ethics
Anti-Plagiarism system
Instructions for Authors
Instructions for Reviewers
Editorial Board
Editorial Office
Contact
Reviewers
All Reviewers
2024
2023
2022
2021
2020
2019
2018
2017
2016
General Data Protection Regulation (RODO)
CASE REPORT
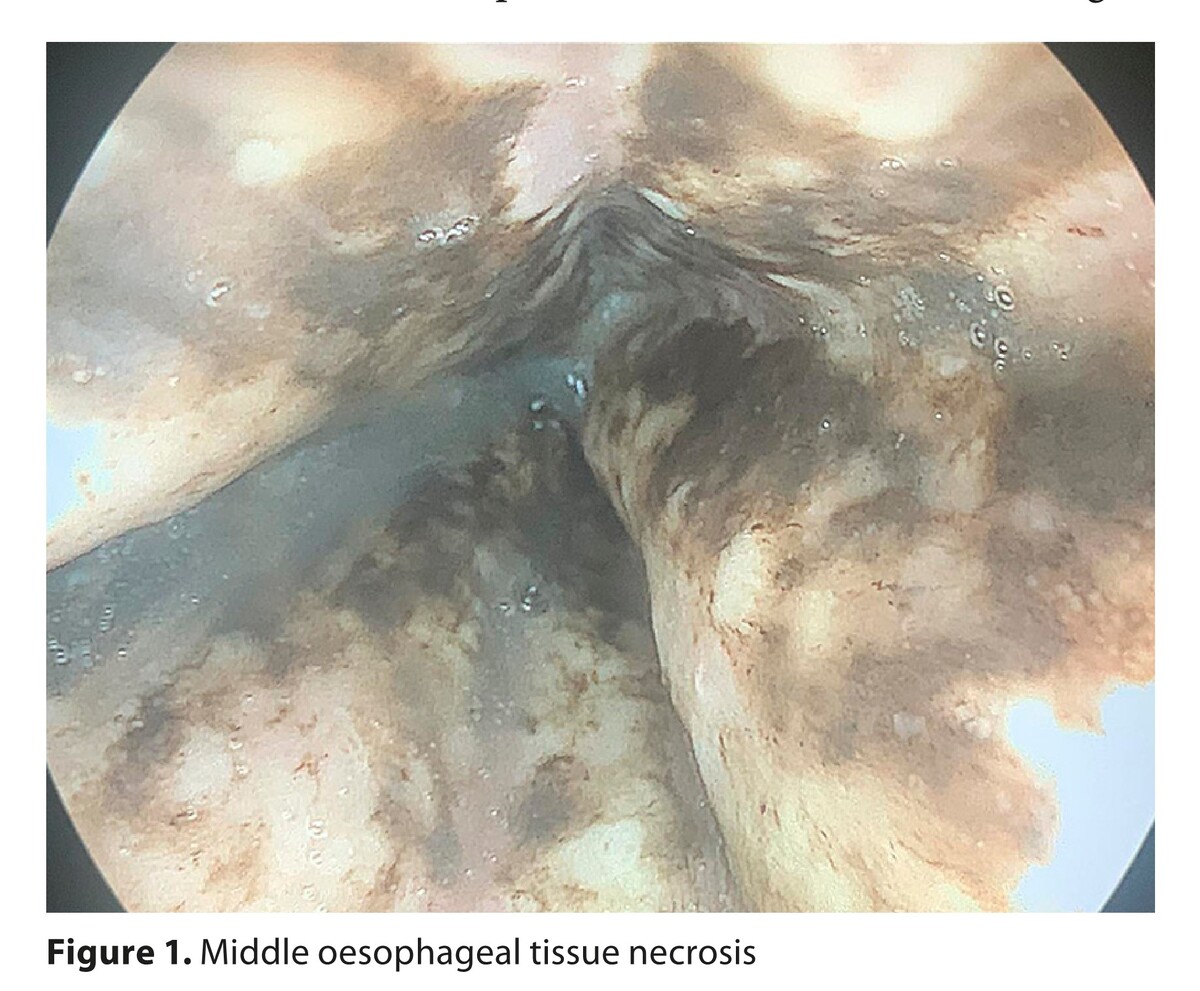
Into the dark of the black oesophagus
1
Department of Gastroenterology with Endoscopy Unit, Medical University, Lublin, Poland
These authors had equal contribution to this work
Corresponding author
Anna Rycyk-Bojarzyńska
Department of Gastroenterology with Endoscopy Unit, Medical University, Lublin, Poland
Department of Gastroenterology with Endoscopy Unit, Medical University, Lublin, Poland
Ann Agric Environ Med. 2024;31(3):450-454
KEYWORDS
black oesophagusGurvit’s syndromeacute oesophageal necrosis (AEN)upper gastrointestinal hemorrhagediabetes mellitus (DM)
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Acute esophageal necrosis (AEN), known as black oesophagus or Gurvit’s syndrome, is an extremely rare clinical syndrome. Patients usually present with life-threatening symptoms of upper gastrointestinal haemorrhage (70–90% of cases), as in this case report. Diagnosis of AEN is confirmed based on oesophagogastroduodenoscopy which reveals diffuse or patchy circumferential black necrotic oesophageal mucosa. The presented patient had some comorbidities, such as poorly controlled diabetes mellitus, secondary to chronic pancreatitis, hypertension, after cholecystectomy, addiction to alcohol and tobacco, and taking a small spoon of baking soda three times a day for a few months because of heartburn. Despite the poor prognosis of AEN, with mortality about 32–35%, most patients present with endoscopic improvement in short time – from 7 days to 1 month. Fortunately, the patient did not to have any complications in the course of AEN, and the treatment was effective.
ABBREVIATIONS
AEN – acute oesophageal necrosis; CMV – cytomegalovirus; CRP – C-reactive protein; DKA – diabetic ketoacidosis; DM – diabetes mellitus; EGD – oesophagogastroduodenoscopy; GFR – glomerular filtration rate; HSV – herpes simplex virus; PPI – proton pomp inhibitor; TPN – total parenteral nutrition
REFERENCES (70)
1.
Lamers CR, Mares WGN, Bac DJ. Black oesophagus: a case series and literature review of acute esophageal necrosis. Scan J Gastroenterol. 2018;53(10–11):1421–1424. doi:10.1080/00365521.2018.1513064.
2.
Vohra I, Attar B, Almoghrabi A. Black Oesophagus Due to Acute Necrosis. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2021;19(2):e16. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2019.12.039.
3.
Siddiqi A, Chaudhary FS, Naqvi HA, Saleh N, Farooqi R, Yousaf MN. Black oesophagus: a syndrome of acute esophageal necrosis associated with active alcohol drinking. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2020;7(1):e000466. doi:10.1136/bmjgast-2020-000466.
4.
Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, New York University Faculty of Medicine, Langone Medical Center, New York, USA, Gurvits GE. Black Oesophagus: Diagnostic Associations and Management Strategies. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2022;33(5). doi:10.5152/tjg.2020.20151.
5.
Ota I, Ono M, Fukuda R, et al. A case of black oesophagus with duodenal involvement. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2021;14(4):975–979. doi:10.1007/s12328-021-01410-w.
6.
Grudell ABM, Mueller PS, Viggiano TR. Black oesophagus: report of six cases and review of the literature, 1963–2003. Diseases of the Oesophagus. 2006;19(2):105–110. doi:10.1111/j.1442-2050.2006.00549.x.
7.
Choksi V, Dave K, Cantave R, et al. “Black Oesophagus” or Gurvits Syndrome: A Rare Complication of Diabetic Ketoacidosis. Case Rep Gastrointest Med. 2017;2017:4815752. doi:10.1155/2017/4815752.
8.
Sunkesula V, Danilewitz M. The Black Oesophagus: A Rare Association. Gastroenterology. 2020;159(4):e8-e10. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.03.078.
9.
Gurvits GE. Black oesophagus: acute esophageal necrosis syndrome. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16(26):3219–3225. doi:10.3748/wjg.v16.i26.3219.
10.
Aranda Escano E, Prieto Calvo M, Perfecto Valero A, Tellaeche de la Iglesia M, Gastaca Mateo M, Valdivieso López A. Black oesophagus after combined liver-kidney transplantation. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;43(1):25–27. doi:10.1016/j.gastre.2019.07.008.
11.
Rossouw J. Hormones, genetic factors, and gender differences in cardiovascular disease. Cardiovascular Res. 2002;53(3):550–557. doi:10.1016/S0008-6363(01)00478-3.
12.
Day A, Sayegh M. Acute oesophageal necrosis: A case report and review of the literature. Inter J Surgery. 2010;8(1):6–14. doi:10.1016/j.ijsu.2009.09.014.
13.
Thomas M, Sostre Santiago V, Suhail FK, Polanco Serra G, Manocha D. The Black Oesophagus. Cureus. 2021;13(10):e18655. doi:10.7759/cureus.18655.
14.
Augusto F, Fernandes V, Cremers MI, et al. Acute Necrotizing Esophagitis: a Large Retrospective Case Series. Endoscopy. 2004;36(5):411–415. doi:10.1055/s-2004-814318.
15.
Uyar S, Duman A, Tan A, et al. Black oesophagus. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2019;30(11):986–987. doi:10.5152/tjg.2019.181019.
16.
Saleem S, Weissman S, Ahmad S. The black oesophagus and duodenum: a rare case report. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2020;13(3):264–267.
17.
Akkinepally S, Poreddy V, Moreno A. Black oesophagus. CCJM. 2009;76(7):400–400. doi:10.3949/ccjm.76a.08102.
18.
Hermet A, Lidove O, Grimbert S, Zeller V, Ducroquet F, Ziza JM. Nécrose aiguë de l’osophage. La Revue de Médecine Interne. 2014;35(6):393–395. doi:10.1016/j.revmed.2013.06.006.
19.
Haddad I, Alomari M, El Kurdi B, Al Momani L, Sanaka MR. A Case of Black Oesophagus. Cureus. 2019;11(9):e5577. doi:10.7759/cureus.5577.
20.
Goldenberg SP, Wain SL, Marignani P. Acute necrotizing esophagitis. Gastroenterol. 1990;98(2):493–496. doi:10.1016/0016-5085(90)90844-q.
21.
Tanaka K, Toyoda H, Hamada Y, et al. A relapse case of acute necrotizing esophagitis. Endoscopy. 2007;39(S 1):E305-E305. doi:10.1055/s-2007-966789.
22.
Aggarwal N, Neupane R, Bhatia U, Singla A, Rana K. Isolated Proximal Black Oesophagus in a COVID-19 Patient. Cureus. 2023;15(3):e36311. doi:10.7759/cureus.36311.
23.
Neumann DA, Francis DL, Baron TH. Proximal black oesophagus: a case report and review of the literature. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. 2009;70(1):180–181. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2008.09.055.
24.
Abdullah HM, Ullah W, Abdallah M, Khan U, Hurairah A, Atiq M. Clinical presentations, management, and outcomes of acute esophageal necrosis: a systemic review. Expert Review of Gastroenterology & Hepatology. 2019;13(5):507–514. doi:10.1080/17474124.2019.1601555.
25.
Chawla GS, Kukova L, Behin DS. Unusual case of acute oesophageal necrosis. BMJ Case Reports CP. 2022;15(2):e248084. doi:10.1136/bcr-2021-248084.
26.
Colón AR, Kamboj AK, Hagen CE, et al. Acute Esophageal Necrosis: A Retrospective Cohort Study Highlighting the Mayo Clinic Experience. Mayo Clinic Proceedings. 2022;97(10):1849–1860. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2022.03.018.
27.
Martins D, Marques R, Costa P, de Sousa JP. The dark side of the oesophagus. Autops Case Rep. 2021;11:e2021284. doi:10.4322/acr.2021.284.
28.
Bonaldi M, Sala C, Mariani P, Fratus G, Novellino L. Black oesophagus: acute esophageal necrosis, clinical case and review of literature. J Surg Case Rep. 2017;2017(3):rjx037. doi:10.1093/jscr/rjx037.
29.
Dziadkoweic KN, Reddy R, Marcus AJ. Acute Esophageal Necrosis Following Acetaminophen Overdose: An Unreported Cause of Black Oesophagus. HCA Healthc J Med. 2022;3(2):47–49. doi:10.36518/2689-0216.1082.
30.
Yuridullah R, Patel V, Melki G, Bollu J. Acute esophageal necrosis masquerading acute coronary syndrome. Autops Case Rep. 2020;10(1):e2019136. doi:10.4322/acr.2019.136.
31.
Rehman O, Jaferi U, Padda I, Khehra N, Atwal H, Parmar M. Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Clinical Manifestations of Acute Esophageal Necrosis in Adults. Cureus. 2021;13(7):e16618. doi:10.7759/cureus.16618.
32.
Katsinelos P, Christodoulou K, Pilpilidis I, et al. Black Oesophagus: An Unusual Finding During Routine Endoscopy. Endoscopy. 2001;33(10):904–904. doi:10.1055/s-2001-17333.
33.
Ali M, Khan N, Yaseen A, Raees A. Gurvits Syndrome: Black Oesophagus in the Postoperative Setting. Cureus. 2022;14(1):e21240. doi:10.7759/cureus.21240.
34.
Jaber F, Alsakarneh S, Sripada S, et al. “Black Oesophagus” or Gurvits Syndrome: A Rare Cause of Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding in Diabetic Ketoacidosis. Cureus. 2023;15(2):e34989. doi:10.7759/cureus.34989.
35.
Haghbayan H, Sarker AK, Coomes EA. Black oesophagus: acute esophageal necrosis complicating diabetic ketoacidosis. CMAJ. 2018;190(35):E1049. doi:10.1503/cmaj.180378.
36.
Ghoneim S, Shah A, Dalal S, Landsman M, Kyprianou A. Black Oesophagus in the Setting of Diabetic Ketoacidosis: A Rare Finding from Our Institution. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2019;13(3):475–480. doi:10.1159/000504434.
37.
Rigolon R, Fossa I, Rodella L, Targher G. Black oesophagus syndrome associated with diabetic ketoacidosis. World J Clin Cases. 2016;4(2):56–59. doi:10.12998/wjcc.v4.i2.56.
38.
Shah AR, Landsman M, Waghray N. A Dire Presentation of Diabetic Ketoacidosis with “Black Oesophagus. Cureus. 2019;11(5):e4761. doi:10.7759/cureus.4761.
39.
Jeyalingam T, Shimamura Y, Teshima C. Endoscopic Resolution of Black Oesophagus With Treatment of Diabetic Ketoacidosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;16(6):e68-e69. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2017.08.046.
40.
Field Z, Kropf J, Lytle M, Castaneira G, Madruga M, Carlan SJ. Black Oesophagus: A Rare Case of Acute Esophageal Necrosis Induced by Diabetic Ketoacidosis in a Young Adult Female. Case Rep Gastrointest Med. 2018;2018:7363406. doi:10.1155/2018/7363406.
41.
Kim YH, Choi SY. Black oesophagus with concomitant candidiasis developed after diabetic ketoacidosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13(42):5662–5663. doi:10.3748/wjg.v13.i42.5662.
42.
Uhlenhopp DJ, Pagnotta G, Sunkara T. Acute esophageal necrosis: A rare case of upper gastrointestinal bleeding from diabetic ketoacidosis. Clin Pract. 2020;10(2):1254. doi:10.4081/cp.2020.1254.
43.
Choksi V, Dave K, Cantave R, et al. “Black Oesophagus” or Gurvits Syndrome: A Rare Complication of Diabetic Ketoacidosis. Case Rep Gastrointest Med. 2017;2017:481575.
44.
Deliwala SS, Hussain MS, Ponnapalli A, Bachuwa G, Gurvits GE. Black ooesophagus, upside-down stomach and cameron lesions: cascade effects of a large hiatal hernia. BMJ Case Reports CP. 2021;14(11):e246496. doi:10.1136/bcr-2021-246496.
45.
Li CJ, Claxton BB, Block P, Reilly S, Manski S, Choudhary C. Acute Esophageal Necrosis Secondary to a Paraesophageal Hernia. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2021;15(2):594–597. doi:10.1159/000517235.
46.
Hwang J, Weigel TL. Acute esophageal necrosis: “black oesophagus.” JSLS. 2007;11(1):165–167.
47.
Matsumoto N, Oki E, Morita M, et al. Successful treatment of acute esophageal necrosis caused by intrathoracic gastric volvulus: report of a case. Surg Today. 2009;39(12):1068–1072. doi:10.1007/s00595-008-3983-4.
48.
Vrba R, Klos D, Kürfurstová D, Špička P. Gastric resection with intrathoracic anastomosis in a hiatal hernia – A case report. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2023;102:107809. doi:10.1016/j.ijscr.2022.107809.
49.
Trappe R, Pohl H, Forberger A, Schindler R, Reinke P. Acute esophageal necrosis (black oesophagus) in the renal transplant recipient: manifestation of primary cytomegalovirus infection. Transplant Infect Dis. 2007;9(1):42–45. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3062.2006.00158.x.
50.
Kroner PT, Chirila R, Purcarea MR, Tribus L, Wadei HM. Acute esophageal necrosis following kidney transplantation. J Med Life. 2021;14(2):284–286. doi:10.25122/jml-2021-0024.
51.
Sheikh AB, Mirza S, Abbas R, et al. Acute Esophageal Necrosis: An In-depth Review of Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Management. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2022;12(1):96–103. doi:10.55729/2000-9666.1020.
52.
Selvaggi F, Cichella A, Aceto GM, Innocenti P, Cotellese R. Acute esophageal necrosis syndrome. The 2021 update from an Italian survey and personal experience. Ann Ital Chir. 2022;93:656–662.
53.
Quitadamo P, Caruso F, Bucci C, et al. Black ooesophagus in an adolescent with type 2 diabetes. Lancet Diab Endocrinol. 2021;9(9):638. doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00187-X.
54.
Khan H, Ahmed M, Daoud M, Philipose J, Ahmed S, Deeb L. Acute Esophageal Necrosis: A View in the Dark. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2019;13(1):25–31. doi:10.1159/000496385.
55.
Sonavane A, Gupta D, Ambekar A, Nagral A. Acute esophageal necrosis: An uncommon entity. J Postgrad Med. 2021;67(2):115–116. doi:10.4103/jpgm.JPGM_635_20.
56.
Dias E, Santos-Antunes J, Macedo G. Diagnosis and management of acute esophageal necrosis. Ann Gastroenterol. 2019;32(6):529–540. doi:10.20524/aog.2019.0418.
57.
Stanko K, Dilmaghani S, Storm A. Acute Esophageal Necrosis Presenting as Acute Blood Loss Anemia. Mayo Clinic Proceedings. 2023;98(1):21–22. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2022.09.004.
58.
Ullah W, Mehmood A, Micaily I, Khan MS. Comprehensive review of acute oesophageal necrosis. BMJ Case Rep. 2019;12(2):e227967. doi:10.1136/bcr-2018-227967.
59.
Inayat F, Hurairah A, Virk HUH. Acute Esophageal Necrosis: An Update. N Am J Med Sci. 2016;8(7):320–322. doi:10.4103/1947-714.187159.
60.
Hong JW, Kim SU, Park HN, Seo JH, Lee YC, Kim H. Black Oesophagus Associated with Alcohol Abuse. Gut Liver. 2008;2(2):133–135. doi:10.5009/gnl.2008.2.2.133.
61.
Gurvits GE, Shapsis A, Lau N, Gualtieri N, Robilotti JG. Acute esophageal necrosis: a rare syndrome. J Gastroenterol. 2007;42(1):29–38. doi:10.1007/s00535-006-1974-z.
62.
Grigore M, Enache I, Chirvase M, et al. Acute Esophageal Necrosis in Acute Pancreatitis—Report of a Case and Endoscopic and Clinical Perspective. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023;13(3):562. doi:10.3390/diagnostics13030562.
63.
Sako A, Kitayama J, Inoue T, Kaizaki S, Nagawa H, Suzuki H. Black ooesophagus—cause? Gut. 2005;54(2):192. doi:10.1136/gut.2004.044784.
64.
Wanta K, Abegunde AT. Tacrolimus-Induced Acute Esophageal Necrosis. ACG Case Rep J. 2020;7(6):e00396. doi:10.14309/crj.0000000000000396.
65.
Brar TS, Helton R, Zaidi Z. Total Parenteral Nutrition Successfully Treating Black Oesophagus Secondary to Hypovolemic Shock. Case Rep Gastrointest Med. 2017;2017:4396870. doi:10.1155/2017/4396870.
66.
Sachar M, Arguetta E, Gurvits GE. Comprehensive Review: Acute Esophageal Necrosis in the Setting of Gastric Volvulus. Dig Dis Sci. 2023;68(5):1672–1676. doi:10.1007/s10620-023-07869-6.
67.
Averbukh LD, Mavilia MG, Gurvits GE. Acute Esophageal Necrosis: A Case Series. Cureus. 2018;10(3):e2391. doi:10.7759/cureus.2391.
68.
Richards J, Wei R, Anjum F. Esophageal Necrosis. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Accessed November 9, 2023. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bo....
69.
Kuiper GM, de Maat MFG, Read MD, et al. Surgical management of a perforated ‘black ooesophagus.’ ANZ J Surg. 2021;91(7–8):E539-E541. doi:10.1111/ans.16565.
70.
Jaiswal P, Araujo JL. Acute Esophageal Necrosis Associated With Acute Pancreatitis. ACG Case Rep J. 2019;6(12):e00295. doi:10.14309/crj.0000000000000295.
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.