Online first
Current issue
Archive
Special Issues
About the Journal
Publication Ethics
Anti-Plagiarism system
Instructions for Authors
Instructions for Reviewers
Editorial Board
Editorial Office
Contact
Reviewers
All Reviewers
2024
2023
2022
2021
2020
2019
2018
2017
2016
General Data Protection Regulation (RODO)
CASE REPORT
Clinical course and neurological sequels after tick-borne encephalitis in children – case report
1
Jan Kochanowski University, Kielce, Poland
2
Collegium Medicum, Jan Kochanowski University, Kielce, Poland
Ann Agric Environ Med. 2022;29(1):162-167
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
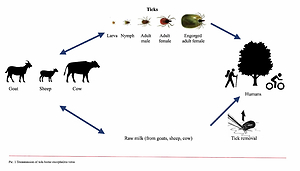
Tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) is a neurotropic, tick-transmitted infection. Clinical presentation ranges from mild aseptic meningitis to severe encephalitis, and may result in long-term neurological sequels.
Objective:
The aim of the study is to present the clinical features of TBE in children, and the laboratory findings, in order to identify neurological sequels and the risk of cognitive deficits in long-term TBE infections.
Material and Methods:
The study included eight children with serologically-confirmed TBE, hospitalized in the Paediatric Centre in Kielce, Poland.
Results:
Despite the more benign clinical course of TBE infections in children compared to adults, the potential for long-term cognitive sequels can be serious. It is hypothesized that a developing CNS is more susceptible to long-term infection effects.
Conclusions:
Paediatric TBE should be considered in children with unexplained acute CNS-related symptoms. The long-term consequences may occur with permanent impairment of the quality of life due to neurological consequences.
Tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) is a neurotropic, tick-transmitted infection. Clinical presentation ranges from mild aseptic meningitis to severe encephalitis, and may result in long-term neurological sequels.
Objective:
The aim of the study is to present the clinical features of TBE in children, and the laboratory findings, in order to identify neurological sequels and the risk of cognitive deficits in long-term TBE infections.
Material and Methods:
The study included eight children with serologically-confirmed TBE, hospitalized in the Paediatric Centre in Kielce, Poland.
Results:
Despite the more benign clinical course of TBE infections in children compared to adults, the potential for long-term cognitive sequels can be serious. It is hypothesized that a developing CNS is more susceptible to long-term infection effects.
Conclusions:
Paediatric TBE should be considered in children with unexplained acute CNS-related symptoms. The long-term consequences may occur with permanent impairment of the quality of life due to neurological consequences.
REFERENCES (31)
1.
Haditsch M. Ticks and tick-borne encephalitis in Europe: Challenges for travel medicine. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2018; 26: 5–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmai....
2.
Estrada-Pena A, Gray JS. Research on the ecology of ticks and tick-borne pathogens--methodological principles and caveats. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2013; (8)3: 29. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.....
3.
Qviller L, Grova L, Viljugrein H, Klingen J, Mysterud A. Temporal pattern of questing tick Ixodes ricinus density at differing elevations in the coastal region of western Norway. Parasit Vectors. 2014; 7: 179. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-3....
4.
Haemig PD, Sjostedt de Luna S, Grafstrom A, et al. Forecasting risk of tick-borne encephalitis (TBE): using data from wildlife and climate to predict next year’s number of human victims. Scand J Infect Dis. 2011; 43: 366–372. https://doi.org/10.3109/003655....
5.
Steffen R. Epidemiology of tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) in international travellers to Western/Central Europe and conclusions on vaccination recommendations. J Travel Med. 2016; 23: 4. https://doi.org/10.1093/jtm/ta....
6.
Dobler G, Gniel D, Petermann R, Pfeffer M. Epidemiology and distribution of tick-borne encephalitis. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2012; 162: 230–238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10354....
7.
Kaiser R. Tick-borne encephalitis. Nervenarzt. 2016; 87(6): 667–680. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00115....
8.
Barp N, Trentini. Clinical and laboratory findings in tick-borne encephalitis virus infection. Parasite Epidemiol Control. 2020; 19: 10: e00160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pare....
9.
Bogovic P, Strle F. Tick-borne encephalitis: a review of epidemiology, clinical characteristics, and management. World J Clin Cases. 2015; (3)5: 430–441. https://doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.....
10.
Buchel K, Bendin J. Repellent efficacy of DEET, Icaridin, and EBAAP against Ixodes ricinus and Ixodes scapularis nymphs. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2015; 6(4): 494–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbd....
11.
Narodowy Instytut Zdrowia Publicznego, Meldunki epidemiologiczne.Choroby zakaźne i zatrucia w Polsce w roku 2019r. http://wwwold.pzh.gov.pl/oldpa....
12.
Bartosik K, Lachowska-Kotowska P. Environmental conditioning of incidence of tick-borne encephalitis in the south-eastern Poland in 1996–2006. Ann Agric Environ Med. 2011; 18(1): 119–126.
13.
ECDC. Tick-borne encephalitis. Annual Epidemiological Report for 2018. https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/....
14.
Steffen R. Tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) in children in Europe. Ticks and Tick-borne Diseases. 2019; 10(1): 100–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbd....
15.
Sundin M. Pediatric tick-borne infections of the central nervous system in an endemic region of Sweden: a prospective evaluation of clinical manifestations Eur J Pediatr. 2012; 171(2): 347–352. https://doi.org/10.1007 s00431-011-1542-2.
16.
Gaieski DF, Nathan BR, O’Brien NF. Emergency neurologic life support: meningitis and encephalitis. Neurocrit Care. 2015; 12(23): S110–S118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028....
17.
Ruzek D, et al. Tick-borne Encephalitis in Europe and Russia: Review of Pathogenesis, Clinical Features, Therapy and Vaccines. Antiviral Res. 2019; 164: 23–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anti....
18.
Schmolck H, Maritz E, Kletzin I, Korinthenberg R. Neurologic, neuro-psychologic, and electroencephalographic findings after European TBE in children. J Child Neurol. 2005; 20(6): 500–508. https://doi.org/10.1177/088307....
19.
Engman ML, Lindstrom K, Sallamba M, Hertz C, Sundberg B, Hansson ME, et al. One-year follow-up of tick-borne central nervous system infections in childhood. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2012; 31: 570–574. https://doi.org/10.1097/inf.0b....
20.
Fowler A, Forsman L, Eriksson M, Wickström R. Tick-borne encephalitis carries a high risk of incomplete recovery in children. J Pediatr. 2013; 163, 555–560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jped....
21.
McNair A, Brown L. Tick-borne encephalitis complicated by monoplegia and sensorineural deafness. J Infect. 1991; 22: 81–86.
22.
Sowula K, Składzie J. Otolaryngological symptoms in patients treated for tick-borne diseases Otolaryngol Pol. 2018 Feb; 72(1): 30–34. https://doi.org/10.5604/01.300....
23.
Sundin M. TBE in children.The Book. Global Health Press, Singapore. 2017. pp. 85–90.
24.
Taba P, Schmutzhard E, Forsberg P. EAN consensus review on prevention, diagnosis and management of tick-borne encephalitis. Eur J Neurol. 2017; 24(10): 1214-e61. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.13....
25.
Czupryna P, Tarasow E, Moniuszko-Malinowska A, et al. MRI and planimetric CT follow-up study of patients with severe tick-borne encephalitis. Infect Dis. 2016; 48: 1–8.
26.
Zawadzki R, et al. Evaluation of imaging methods in tick-borne encephalitis. Pol J Radiol. 2017; 82: 742–747. https://doi.org/10.12659/pjr.9....
27.
Beck R. Fritz K. Molecular basis of the divergent immunogenicity of two pediatric tick-borne encephalitis virus vaccines. J Virol. 2016; 90: 4.1964–1972. https://dx.doi.org/10.1128%2FJ....
28.
Zavadska D, Anca I. Recommendations for tick-borne encephalitis vaccination from the Central European Vaccination Awareness Group (CEVAG). Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2013; 9(2): 362–374. https://doi.org/10.4161/hv.227....
29.
Galgani I, Bunge E. Systematic literature review comparing rapid 3-dose administration of the GSK tick-borne encephalitis vaccine with other primary immunization schedules. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2017; 16: 919–932. https://doi.org/10.1080/147605....
30.
Szczepienia ochronne w Polsce w 2018 roku. Biuletyn Narodowego Instytutu Zdrowia Publicznego–Państwowego Zakładu Higieny. http://wwwold.pzh.gov.pl/oldpa....
31.
Erber W, Schmitt HJ. Self-reported tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) vaccination coverage in Europe: Results from a cross-sectional study. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2018; 9(4): 768–777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbd....
Share
RELATED ARTICLE